If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with megaloblastic anemia, there is hope. Our comprehensive plan includes expert insights on diagnosis, treatment, and management to help you effectively address this condition and improve your quality of life.
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia that is characterized by abnormally large red blood cells. It is often caused by a deficiency in vitamin B12 or folate, which can affect the production of these cells in the bone marrow. Without proper treatment, megaloblastic anemia can lead to a range of complications, including nerve damage, cardiovascular issues, and fertility problems.
Our plan is designed to provide a comprehensive resource for those living with megaloblastic anemia, offering insights into the underlying causes, diagnostic methods, and effective treatment options.
Key Features:
- Our comprehensive megaloblastic anemia plan includes expert insights on diagnosis, treatment, and management.
- Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia that is characterized by abnormally large red blood cells and can lead to various complications.
- Proper treatment is essential for managing megaloblastic anemia and improving quality of life.
- The plan provides insights into underlying causes, diagnostic methods, and effective treatment options.
- Effective management involves lifestyle changes, nutritional considerations, and ongoing monitoring and follow-up care.
Diagnosing Megaloblastic Anemia
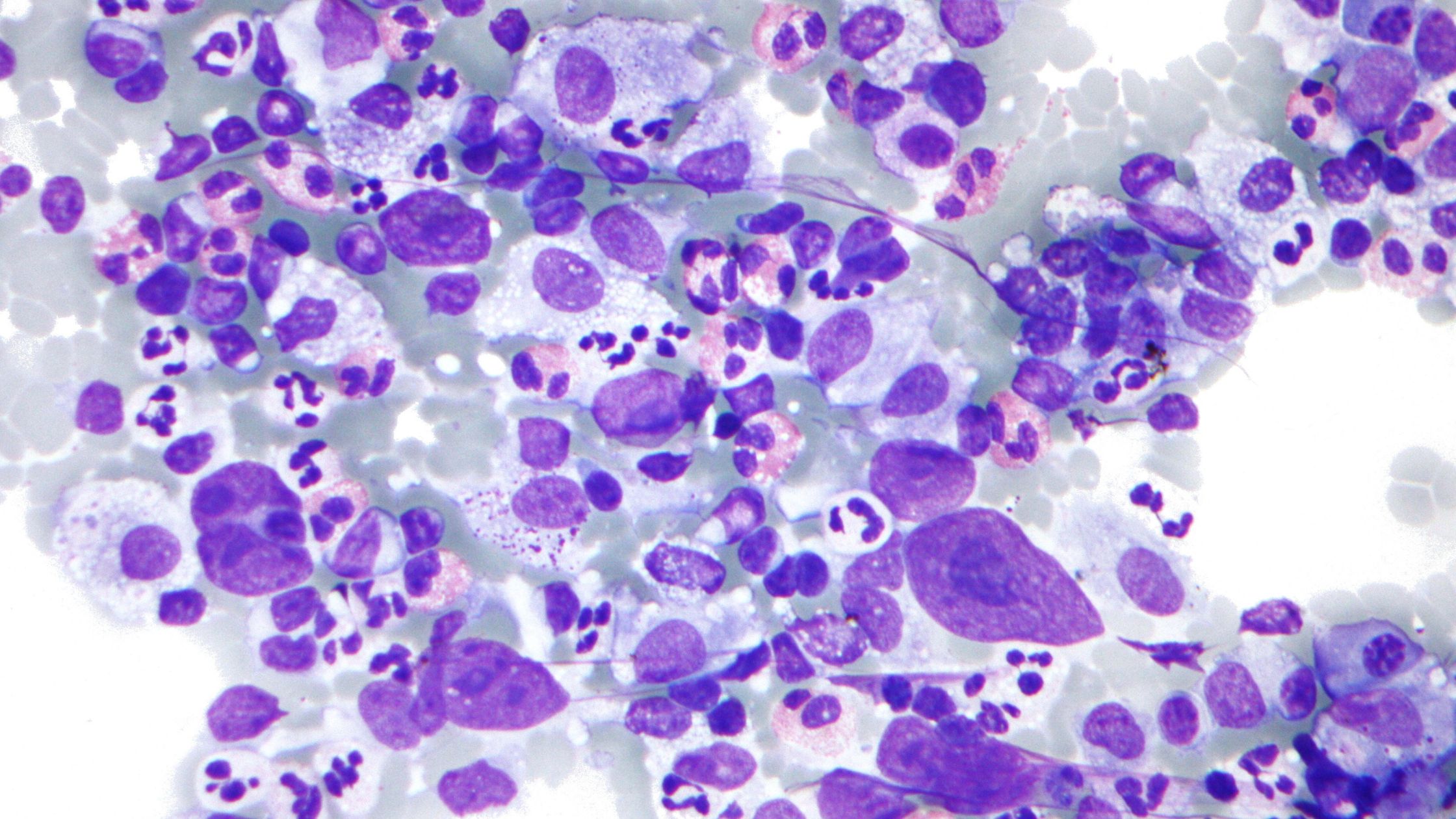
Diagnosis of megaloblastic anemia usually involves a complete blood count (CBC) test and measurement of vitamin B12 and folate levels in the blood. In some cases, a bone marrow examination may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause of the condition.
Causes of Macrocytic Anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia, but other conditions can also cause macrocytosis. These include liver disease, hypothyroidism, and alcohol abuse. It is essential to differentiate between the different causes of macrocytic anemia to determine the appropriate treatment.

Treating Megaloblastic Anemia
Treatment of megaloblastic anemia involves correcting the underlying nutrient deficiency through dietary changes and supplements. Vitamin B12 injections or oral supplements are the most common treatment options. Folate supplements may also be prescribed depending on the underlying cause of the deficiency. In severe cases or if the patient is unable to absorb the nutrients, medical interventions such as blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants may be necessary.
Complications of Megaloblastic Anemia
If left untreated, megaloblastic anemia can lead to severe complications, including nerve damage, cardiovascular disease, and fertility problems. Proper management and treatment are essential in preventing these complications.
Understanding the basics of megaloblastic anemia, including its causes and diagnosis, is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan. By addressing the underlying nutrient deficiency and managing the condition, patients can improve their overall health and well-being.
Exploring Acute Megaloblastic Anemia
Acute megaloblastic anemia is a condition that requires prompt medical attention due to its potential complications. This is a severe form of megaloblastic anemia, which is characterized by an enlarged and immature red blood cell formation.
The symptoms of acute megaloblastic anemia are similar to those of other types of anemia, such as fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. However, acute cases can also present with severe chest pain, shortness of breath, and confusion.
Diagnosis of acute megaloblastic anemia is usually made through a blood test that measures the levels of vitamin B12 and folate in the blood. In cases where the initial test results are inconclusive, a bone marrow examination may be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for acute megaloblastic anemia usually involves blood transfusions to provide the body with healthy red blood cells. Additionally, vitamin B12 and folate supplements may be prescribed to support the formation of new red blood cells.
Management Strategies for Acute Megaloblastic Anemia
Following an acute episode of megaloblastic anemia, it is essential to take steps to prevent future episodes and manage the underlying cause of the condition. Strategies that can be helpful in managing acute megaloblastic anemia include:
- Identifying and addressing any underlying conditions that may contribute to megaloblastic anemia, such as pernicious anemia or alcoholism.
- Focusing on a nutrient-dense diet that is high in vitamin B12, folate, and other essential nutrients.
- Avoiding alcohol and smoking, which can worsen the symptoms of megaloblastic anemia.
- Staying hydrated and getting enough rest to support the formation of healthy red blood cells.
“Prompt medical attention and effective management are essential to preventing complications associated with acute megaloblastic anemia”
It is important to closely monitor the condition and work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan that takes into account individual needs and circumstances.
In conclusion, acute megaloblastic anemia is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention and careful management. By following a comprehensive management plan, individuals can effectively address the condition and prevent future episodes.
Alcohol and Megaloblastic Anemia
Alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on the development and progression of megaloblastic anemia. The relationship between alcohol and megaloblastic anemia is linked to the way alcohol affects the absorption and utilization of essential nutrients in the body, such as vitamin B12 and folate.
Alcohol consumption can directly damage the lining of the stomach and intestines, reducing the body’s ability to absorb these nutrients from the diet. Additionally, alcohol abuse can lead to poor dietary choices and malnutrition, further exacerbating the development of megaloblastic anemia.
Alcohol and the Absorption of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells and DNA synthesis. However, the body cannot produce vitamin B12, and it must be obtained from dietary sources or supplements.
Alcohol can impair the body’s ability to absorb vitamin B12 from the diet. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to gastritis, inflammation of the stomach lining, and damage to the parietal cells in the stomach. These cells produce intrinsic factor, a protein that binds to vitamin B12 and facilitates its absorption from the small intestine into the bloodstream. Damage to the parietal cells can lead to reduced intrinsic factor production, impairing vitamin B12 absorption and leading to a deficiency.
Alcohol and the Absorption of Folate
Folate is also crucial for the production of red blood cells and the synthesis of DNA. However, the body cannot store folate, and it must be obtained from dietary sources.
Alcohol consumption can impair the body’s ability to absorb folate from the diet. Heavy alcohol consumption can lead to inflammation of the small intestine, reducing the absorption of folate and other essential nutrients.
Managing Alcohol-Related Megaloblastic Anemia
The first step in managing megaloblastic anemia related to alcohol consumption is to stop drinking alcohol. This can help reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract and improve the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients.
In addition to stopping alcohol consumption, dietary changes and supplements may be necessary to address nutrient deficiencies. Vitamin B12 and folate supplements may be prescribed to increase the levels of these essential nutrients in the body. Dietary changes, such as increasing the consumption of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, can also support optimal nutrient intake.
Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to developing an effective plan for managing megaloblastic anemia related to alcohol consumption. With proper treatment and management, individuals with alcohol-related megaloblastic anemia can achieve optimal health outcomes and reduce the risk of further complications.
Causes of Macrocytic Anemia
Macrocytic anemia can be caused by various underlying factors, including megaloblastic anemia and pernicious anemia. Understanding the specific causes of macrocytic anemia is crucial in developing an optimal treatment plan.
Megaloblastic anemia is primarily caused by a deficiency in vitamin B12 or folate, both of which are essential for red blood cell production. Without these nutrients, red blood cells cannot properly mature, leading to the characteristic large size (macrocytosis). Pernicious anemia, on the other hand, is caused by an autoimmune condition that attacks the body’s ability to absorb vitamin B12.
Other potential causes of macrocytic anemia include liver disease, thyroid disorders, and alcoholism. Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and anticonvulsants, can also cause macrocytosis.
Comparison of Megaloblastic Anemia and Pernicious Anemia
| Megaloblastic Anemia | Pernicious Anemia | |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Deficiency in vitamin B12 or folate | Autoimmune condition that attacks the body’s ability to absorb vitamin B12 |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, numbness and tingling in hands and feet | Fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, tingling and numbness in the hands and feet, difficulty walking, loss of appetite, weight loss |
| Treatment | Supplementation with vitamin B12 or folate, dietary changes | Vitamin B12 injections or nasal spray, dietary changes |
Megaloblastic Anemia Treatment Options
Effective treatment of megaloblastic anemia requires a comprehensive approach that involves addressing the underlying causes and providing optimal support to improve overall health. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include dietary changes, supplementation, and medical interventions.
Dietary Changes
For individuals with megaloblastic anemia, a diet rich in essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, folate, and iron is crucial. Consuming foods such as lean meats, leafy greens, and fortified cereals can help increase nutrient intake and support red blood cell production. A registered dietitian can provide guidance in developing a balanced and nutrient-dense meal plan.
Supplementation
In addition to dietary changes, supplementation with vitamin B12 and/or folate may be necessary to address nutrient deficiencies. Supplements can be taken orally or administered via injection, depending on individual needs. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of supplementation.
Medical interventions
In severe cases of megaloblastic anemia, medical interventions such as blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants may be necessary. These interventions should be considered as a last resort and only when other treatment options are not effective.
It is important to note that megaloblastic anemia may not have a cure, and treatment is focused on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Signs and Symptoms of Megaloblastic Anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a condition characterized by abnormally large red blood cells. The signs and symptoms of megaloblastic anemia may not appear immediately and can vary in severity. Some of the common symptoms associated with this condition include:
- Fatigue: A persistent feeling of tiredness that cannot be explained by other factors.
- Weakness: Difficulty in performing daily tasks due to muscle weakness.
- Pale skin: A decrease in the red blood cells can lead to pale or yellowish skin.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty in breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Headaches: Chronic headaches may be a symptom of megaloblastic anemia.
- Tingling and numbness: A sensation of tingling or numbness in the hands and feet may occur due to nerve damage.
In addition to these symptoms, those with megaloblastic anemia may also experience mood changes, difficulty concentrating, and rapid heart rate.
In severe cases, megaloblastic anemia can lead to neurological damage, including confusion, memory loss, and even seizures.
It is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. A blood test can help diagnose megaloblastic anemia, and early detection can aid in better management of this condition.
Diagnosis of Megaloblastic Anemia
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of megaloblastic anemia. A comprehensive diagnostic workup includes:
- A complete blood count (CBC) to detect macrocytosis
- Peripheral blood smear to look for megaloblastic changes in the red blood cells
- Serum vitamin B12 and folate levels to determine deficiencies
- Bone marrow examination to confirm the diagnosis
- Other diagnostic tests to identify underlying causes, such as pernicious anemia or alcoholism
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the focus shifts to creating a personalized megaloblastic anemia treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Note: Megaloblastic anemia can be misdiagnosed as iron-deficiency anemia because both conditions share similar symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. However, iron supplementation can worsen megaloblastic anemia and should be avoided until the diagnosis is confirmed.
Nutritional Considerations for Megaloblastic Anemia
The importance of proper nutrition cannot be overstated in managing megaloblastic anemia. A diet that is rich in certain essential nutrients can help ensure healthy blood cell formation and optimal treatment outcomes.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is one of the critical components necessary for red blood cell production. It is found primarily in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy. However, for some individuals, their bodies may not effectively absorb vitamin B12. In such cases, supplementation may be necessary. For optimal absorption, vitamin B12 supplements may be given orally or through injections.
Folate
Folate is another essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in red blood cell production. It is commonly found in leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, and fortified grains. For individuals who have difficulty absorbing this nutrient, supplements may be effective.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is known to enhance iron absorption, which is critical in ensuring healthy red blood cell formation. Food sources rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, tomatoes, and leafy green vegetables. In addition to dietary sources, some individuals may require supplementation to meet their nutritional needs.
Iron
Iron is a critical component for hemoglobin synthesis, which is necessary for the transportation of oxygen throughout the body. Iron-rich foods include red meat, poultry, fish, beans, and lentils. In cases of iron deficiency, supplements may be required. However, excessive iron intake can lead to iron overload, so it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before taking iron supplements.
In conclusion, a comprehensive megaloblastic anemia plan includes proper nutrition. Nutritional considerations should be taken seriously as they play an integral role in the effective management of this condition. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or starting on any supplements.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Megaloblastic Anemia
Managing megaloblastic anemia requires a multifaceted approach that includes medical interventions, nutritional adjustments, and lifestyle changes. In this section, we will explore the importance of lifestyle changes and how they can contribute to better management of this condition.
Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for optimal management of megaloblastic anemia. This includes getting enough rest, regular exercise, and managing stress. Sleep is crucial for cell regeneration and the production of healthy red blood cells, so it’s important to aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night. Exercise can also stimulate the production of red blood cells, so incorporating it into your routine can have positive effects.
Managing Stress
Stress can lead to a variety of health issues and can exacerbate megaloblastic anemia symptoms. Identifying and managing stress is essential for long-term management of this condition. There are many techniques that can help manage stress, such as meditation, breathing exercises, or even therapy.
Dietary Changes
In addition to medical and lifestyle interventions, dietary changes can also contribute to better management of megaloblastic anemia. Increasing your intake of vitamin B12 and folic acid can help prevent anemia and promote the production of healthy red blood cells. This can be achieved by incorporating foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fortified cereals into your diet.
| Foods rich in Vitamin B12 | Foods rich in Folate |
|---|---|
| Beef liver | Spinach |
| Clams | Black-eyed peas |
| Tuna | Asparagus |
| Fish | Brussels sprouts |
| Fortified cereals | Lentils |
Ensuring a balanced and diverse diet can help provide the necessary nutrients for megaloblastic anemia treatment. Working with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can be helpful in developing a personalized nutrition plan.
By making lifestyle changes, such as managing stress, getting regular exercise, and incorporating healthy foods into your diet, you can support your body’s ability to manage megaloblastic anemia and improve your overall health and well-being.
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
After the initial diagnosis and treatment, ongoing follow-up care and monitoring are essential for long-term management of megaloblastic anemia. This ensures timely detection of any relapse or complications, and adjustments to the management plan can be made accordingly.
Recommended Follow-up Protocol
The recommended follow-up protocol for megaloblastic anemia patients involves regular check-ups with a healthcare provider. The frequency of these appointments will depend on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment. However, it is generally recommended that patients have follow-up appointments every three to six months initially, with the frequency decreasing over time if the condition is well-managed.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and detecting any signs of relapse or complications. During these appointments, your healthcare provider may perform blood tests to check your iron levels, red blood cell count, and vitamin B12 and folate levels. They may also conduct a physical examination to check for any signs of complications, such as neurological symptoms.
Self-Monitoring
In addition to regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, self-monitoring can also be beneficial. This involves keeping track of your symptoms and monitoring your diet and lifestyle. By doing so, you can identify any changes that may impact your megaloblastic anemia management plan and take action accordingly.
Adjustments to the Megaloblastic Anemia Plan
If any issues or complications arise during follow-up care and monitoring, adjustments to the megaloblastic anemia plan may need to be made. For example, if vitamin B12 levels are found to be low, supplementation may need to be increased. It is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to ensure that any necessary adjustments are made promptly and effectively.
Support and Resources for Megaloblastic Anemia Patients
Living with megaloblastic anemia can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. However, there are various support systems and resources available to help you navigate this condition. Below are some of the options you may find helpful:
Support Groups
Support groups can provide a safe and supportive environment for you to connect with others who are experiencing similar challenges. They can offer practical advice, emotional support, and a sense of community. Some resources for finding support groups include:
- The National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD)
- The American Society of Hematology (ASH)
- The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society
Online Communities
Online communities can be a useful source of information and support, particularly for those who may not have access to in-person support groups. Some popular online communities include:
- The Megaloblastic Anemia Support Group on Facebook
- The Megaloblastic Anemia subreddit on Reddit
The National Hemophilia Foundation
The National Hemophilia Foundation is a non-profit organization dedicated to supporting individuals with bleeding disorders, including megaloblastic anemia. They offer resources such as educational materials, assistance with insurance navigation, and a patient assistance program to help with medication costs.
Your Healthcare Team
Don’t forget that your healthcare team can also be an excellent source of support and information. They can answer your questions, provide guidance on managing symptoms, and connect you with additional resources in your area.
Remember, you don’t have to face megaloblastic anemia alone. Reach out to others for support and resources.
Potential Complications of Megaloblastic Anemia
Megaloblastic anemia, if left unmanaged, can lead to various complications that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. Some of the potential complications of megaloblastic anemia include:
- Nerve damage: Megaloblastic anemia can damage the myelin sheath that protects nerves, leading to tingling, numbness, and weakness in the limbs.
- Cardiovascular issues: Megaloblastic anemia can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, as it can cause high homocysteine levels.
- Fertility problems: Megaloblastic anemia can lead to problems with fertility in both men and women, as it can affect the production and quality of sperm and eggs.
It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you may have megaloblastic anemia to prevent these complications from occurring.
Managing the Risk of Complications
While megaloblastic anemia can lead to various complications, proactive management can help reduce the risk.
Patients with megaloblastic anemia should ensure they follow an optimal management plan that includes dietary changes, medical interventions, and lifestyle modifications. Patients with chronic megaloblastic anemia should also undergo regular follow-up care and monitoring to detect any relapse or development of complications.
Additionally, patients should seek support and resources available to them, such as support groups and online communities, to help them manage the condition and the risk of complications.
“Megaloblastic anemia can lead to severe complications if left unmanaged, but proactive management can help reduce the risk and improve patient outcomes.”
By following an optimal megaloblastic anemia plan and seeking the appropriate support and care, patients can effectively manage their condition and avoid the potential complications associated with it.
Emerging Research and Future Perspectives
Medical research is continuously advancing, and new findings can impact the management of megaloblastic anemia. Recent research has shed light on the impact of genetic factors in the development of megaloblastic anemia, leading to the development of new diagnostic tools and treatment options.
Advancements in gene editing and regenerative medicine have also opened up new possibilities for treating megaloblastic anemia. Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells to regenerate damaged or deficient blood cells, potentially leading to a cure for the condition.
Another area of emerging research is the exploration of alternative treatment options for megaloblastic anemia. Traditional Chinese medicine, for example, has been shown to have positive effects in managing the condition, and researchers are investigating the use of other natural remedies and supplements to complement conventional treatment.
Overall, the future of megaloblastic anemia management looks promising, with continued advancements in research and treatment options paving the way for more effective and personalized care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, megaloblastic anemia is a complex condition that requires careful management and attention. Our comprehensive plan offers insights into the diagnosis, treatment, and management of this condition, providing a valuable resource for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Takeaways
Key takeaways from our megaloblastic anemia plan include:
- Understand the underlying causes and symptoms of megaloblastic anemia
- Seek prompt medical attention for acute cases
- Avoid alcohol consumption to mitigate its impact on megaloblastic anemia
- Explore available treatment options, including dietary adjustments and medical interventions
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle to support optimal outcomes
- Stay informed about potential complications and engage in ongoing monitoring and follow-up care
- Connect with support groups and resources to navigate this condition effectively
- Stay up-to-date on emerging research and future perspectives in megaloblastic anemia management
By incorporating these insights into your management plan, you can take proactive steps towards improving your health and well-being, and effectively managing megaloblastic anemia.
FAQ
What is megaloblastic anemia?
Megaloblastic anemia is a condition characterized by the production of abnormally large, immature red blood cells in the bone marrow. It is typically caused by a deficiency in vitamin B12 or folate.
How is megaloblastic anemia diagnosed?
Megaloblastic anemia can be diagnosed through blood tests that measure the levels of vitamin B12 and folate, as well as by examining the size and shape of the red blood cells under a microscope.
What are the common symptoms of megaloblastic anemia?
Common symptoms of megaloblastic anemia include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and neurological symptoms like numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
How is megaloblastic anemia treated?
Treatment for megaloblastic anemia typically involves supplementing with vitamin B12 and/or folate to correct the underlying deficiency. In some cases, additional treatments such as blood transfusions or medication may be necessary.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage megaloblastic anemia?
Yes, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage megaloblastic anemia. These may include adopting a balanced diet rich in foods high in vitamin B12 and folate, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress.
Can megaloblastic anemia be cured?
In most cases, megaloblastic anemia can be effectively managed through proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments. However, in some cases, the underlying cause of the condition may be chronic and require ongoing management.
What are the potential complications of megaloblastic anemia?
If left untreated or poorly managed, megaloblastic anemia can lead to complications such as nerve damage, cardiovascular issues, and fertility problems. That’s why it is important to seek timely and appropriate medical care.
Where can I find support and resources for megaloblastic anemia?
There are various support groups, online communities, and resources available for individuals with megaloblastic anemia. These can provide valuable information, guidance, and a sense of community.